If you are researching term life insurance, chances are you want maximum protection at the lowest cost—without complexity. You are not alone. Term life insurance is the most purchased life insurance policy in the United States, especially among working families, homeowners, and young professionals.
This guide explains term life insurance in plain English—what it is, how it works, its advantages, disadvantages, and what it really costs—so you can decide if it fits your financial plan.
👉 New to life insurance? Start with our complete guide:
Life Insurance Explained: Types, Benefits, Costs, and How to Choose the Right Policy
Protection First — Key Takeaway
Financial growth only works when what you build is protected. Life insurance and risk management form the foundation of every sound financial plan, ensuring income, family, and long-term goals stay secure through life’s uncertainties.
What Is Term Life Insurance?
Term life insurance is a type of life insurance that provides coverage for a specific period of time, called a term. Common terms are:
- 10 years
- 20 years
- 30 years
If the insured person passes away during the term, the policy pays a tax-free death benefit to the beneficiaries. If the term expires and the insured is still alive, the policy simply ends—no payout, no cash value.
Simple Definition:
Term life insurance is temporary life insurance designed to protect your loved ones during your most financially vulnerable years.
How Does Term Life Insurance Work?
Term life insurance works in a very straightforward way:
- You choose the coverage amount (e.g., $250,000, $500,000, $1 million)
- You choose the term length (10, 20, or 30 years)
- You pay a fixed monthly or annual premium
- If you pass away during the term, your beneficiaries receive the death benefit
- If you outlive the term, coverage ends unless renewed or converted
Because it is simple and predictable, term life insurance is often recommended as a foundation policy in a financial plan.
To better understand flexibility, cash value growth, and long-term planning benefits, it helps to review how universal life insurance works within a broader financial strategy.
Who Should Consider Term Life Insurance?
Term life insurance is ideal for people who need high coverage at a low cost for a specific period of life.
It is especially suitable for:
- Parents with young children
- Homeowners with a mortgage
- Income earners supporting a family
- Business owners with temporary liabilities
- Professionals early in their careers
- Anyone seeking affordable life insurance
If someone depends on your income, term life insurance protects that income.
Every one has different financial needs depending on their age, responsibilities and other life styles. It is very important to understand how much life insurance you need.
Pros of Term Life Insurance
1. Affordable Premiums
Term life insurance offers the highest coverage for the lowest cost compared to other life insurance types.
2. Simple and Easy to Understand
There are no investments, cash values, or complex calculations—just pure protection.
3. Flexible Coverage Amounts
You can purchase large policies (even $1M+) at a fraction of the cost of permanent insurance.
4. Ideal for Temporary Needs
Perfect for covering:
- Mortgage payments
- Child education costs
- Income replacement
- Business loans
5. Fixed Premiums
Most term policies lock in premiums for the entire term, making budgeting easy.
Cons of Term Life Insurance
1. No Cash Value
Unlike whole life insurance, term life insurance does not build savings or investment value.
2. Coverage Ends
If you outlive the policy, the coverage expires unless renewed—often at a higher cost.
3. Increasing Cost with Age
Renewing term insurance later in life can become expensive due to age and health changes.
4. Temporary Protection Only
It does not provide lifelong coverage unless converted.
Term Life Insurance Cost: What Affects the Price?
The cost of term life insurance depends on several factors:
Key Pricing Factors:
- Age (younger = cheaper)
- Health condition
- Gender
- Smoking status
- Coverage amount
- Term length
- Lifestyle risks
Average Monthly Cost (Approximate)
| Age | Coverage | Term | Monthly Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | $500,000 | 20 years | $20–$30 |
| 40 | $500,000 | 20 years | $35–$55 |
| 50 | $500,000 | 20 years | $90–$150 |
Healthy non-smokers typically qualify for the best rates.
Term Life Insurance vs Whole Life Insurance
| Feature | Term Life Insurance | Whole Life Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage Duration | Temporary | Lifetime |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Cash Value | No | Yes |
| Complexity | Simple | More complex |
| Best For | Income protection | Wealth & legacy planning |
For many families, term life insurance covers protection needs, while permanent policies serve long-term wealth strategies.
Can You Convert Term Life Insurance?
Yes. Many policies offer a conversion option, allowing you to convert term life insurance into permanent life insurance without new medical underwriting.
This feature adds flexibility if your financial goals change.

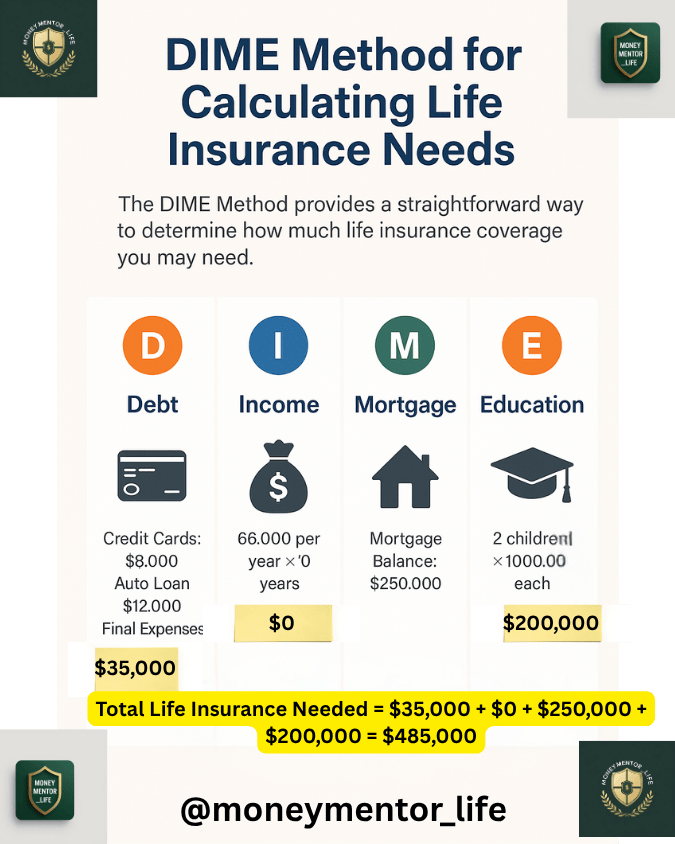
How Much Term Life Insurance Do You Need?
A common rule of thumb is:
10–15 times your annual income
However, a better approach considers:
- Outstanding debts
- Mortgage balance
- Education expenses
- Living costs for dependents
- Existing savings and investments
A licensed financial professional can help determine the right amount.
Is Term Life Insurance Worth It?
For most people, yes.
Term life insurance delivers:
- High coverage
- Low premiums
- Clear purpose
- Strong financial protection
It is often the smartest first life insurance policy and a core component of responsible financial planning.

Education builds clarity. Personalized planning provides direction. If you want to understand how these strategies apply to your financial goals, a thoughtful review can help you move forward with confidence.
Explore Your OptionsFrequently Asked Questions (AEO-Optimized)
Is term life insurance good for families?
Yes. It is designed to replace income and protect dependents during working years.
What is better? Term life insurance or final expense insurance?
What happens if I outlive my term life insurance?
Is term life insurance tax-free?
Yes. Death benefits are generally paid tax-free to beneficiaries.
Can I buy term life insurance online?
Yes, many insurers offer online applications, though professional guidance can improve policy fit.
👉 To understand how term life insurance fits into the bigger picture, read our complete guide:
Life Insurance Explained: Types, Benefits, Costs, and How to Choose the Right Policy
Final Thoughts
The policy expires. You may renew, convert, or purchase a new policy.
Term life insurance is not about investment or complexity—it is about responsibility and protection. When chosen correctly, it provides peace of mind at an affordable cost and protects what matters most.